During pregnancy, your body will go through many changes. Though some of these changes will be discussed at your prenatal visits, most changes will not be addressed unless you express a particular concern.
Routine prenatal visits are short (about 15 minutes). Each time very specific clinical information (weight, blood pressure, fetal heart rate, etc.) is obtained, leaving little time to talk about what is on your mind. To deal with this time constraint, it is best to learn as much as you can on your own so you can spend the time you have most efficiently.
We will discuss many of the physical and hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy … but the list is long. Take time to research the more common maternal body changes. (Source) If you do this you will feel more prepared to discuss them with your provider.
This post contains affiliate links. You can read our affiliate disclaimer at the bottom of this post.

This post contains affiliate links. You can read our affiliate disclaimer at the bottom of this post.
This goal of this article is to help explain some of the ways pregnancy affects your body an all-inclusive list of maternal body changes during pregnancy. We have included the physical and functional changes you may experience and perhaps, more importantly, we have included lots of tips and links to other articles and products that will help you feel more comfortable as you grow a tiny human!
It is important to understand that these changes (with very few exceptions) will resolve postpartum.
Body Changes During Pregnancy:
Heart Function
During pregnancy, the total amount of blood your heart pumps in one minute (cardiac output) increases by up to 40%. This is truly remarkable considering the fact that a woman’s cardiac output when not pregnant is approximately 5 liters per minute.
There are a few factors that contribute to this dramatic increase in blood supply to support fetal development:
- Maternal blood volume increases by 50%
- Heart rate on up to 20 beats per minute.
- The stroke volume (the amount of blood the heart pumps with each heartbeat) increases. (Source)
There is a significant increase in the amount of blood the heart pumps during pregnancy. What is interesting is how this increase in blood flow can rapidly decrease if the blood return to the heart through the large inferior vena cava (IVC) is impaired in any way.
The most common clinical example of this is often observed when a pregnant woman lies on her back. The compression of the IVC causes can decrease the mother’s blood pressure and will decrease the fetal heart rate. This is why pregnant women are told to lie on their left side. Why Left Side Sleep During Pregnancy Is Best
Anemia is also an important topic to discuss when it comes to cardiovascular changes since anemia directly affects the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood to the fetus. There are many causes of anemia.
If you are diagnosed with iron-deficient anemia, your provider will prescribe iron during your pregnancy. Iron should be avoided with certain forms of anemia, so it is important to check with your provider. What Every Pregnant Woman Needs To Know About Anemia
Lung Volume
There are two ways we move air in and out of our lungs:
- Abdominal Breathing – also called diaphragmatic breathing occurs when the diaphragm moves downward.
- Chest Breathing – occurs when the chest or ribcage expands. This breathing is more shallow than abdominal breathing.
During pregnancy, as the uterus enlarges it pushes the diaphragm as much as 4 centimeters. This occurs during the latter stages of pregnancy and decreases lung volume. (Source)
To compensate for this decrease in lung volume, the ligaments around the ribs loosen and the chest wall muscles relax. This allows for greater expansion of the chest wall. In addition, the respiratory rate (breaths/minute) increases to maintain normal oxygen delivery for fetal development.
Kidney/Urinary Tract Changes
The maternal kidneys go through significant changes during pregnancy. The kidneys enlarge as a result of the increased blood volume being filtered by the kidneys during pregnancy.
The bladder capacity and size of the ureters and renal pelvis increase in size. This is a result of hormonal relaxation of the smooth muscle in the walls of these structures.
The enlargement of the urinary tract increases the risk of urinary tract infections. Infections occur because urine is able to pool in the enlarged urinary tract. By the 20th week of pregnancy, the uterus reaches the level of the pelvic brim and compresses the ureter which carries urine to the bladder. and cause a kidney infection (Pyelonephritis).
Because of the position of the uterus, the right kidney is affected more often.
Skin Changes
During pregnancy, the melanocyte-stimulating hormone increases as does the estrogen hormone. These hormones increase the stimulation of the pigment-producing cells called melanocytes.
Increased pigmentation in the face is also referred to as the “mask of pregnancy”. The nipples and areola also darken. Many women will also observe the development of a dark line down their stomachs in the midline. This is called the linea nigra.
Moles can also darken and clearly this is a change that has to be discussed with your provider to be sure it is the result of the hormonal changes during pregnancy and not cancerous changes.
Skin exposure to the sun should be limited during pregnancy.
Metabolism and Weight Changes:
Weight gain during pregnancy averages between 25 and 35 pounds. However, women who are considered obese (based on BMI) need not gain any weight or may even lose weight.
Women who are below what is considered a normal BMI should gain weight as this can impact normal fetal growth.
To check your BMI use this following link: CLICK HERE (Courtesy of calculator.net)
Metabolism can increase by as much as 20% during pregnancy, most of this occurring during the third trimester.
Digestive Changes
When discussing body changes during pregnancy, digestive changes are quite common. Most of these changes are due to the hormone: progesterone.
Progesterone relaxes smooth muscle along the intestinal tract. Relaxation of this muscle slows down the intestine.
This smooth muscle relaxation also affects the stomach, delaying the emptying of gastric contents. It is interesting to note that this is why labor and delivery staff prefer laboring patients not have a full stomach, should there be a need for general anesthesia.
Heartburn is another digestive change during pregnancy. Progesterone relaxes the esophageal sphincter allowing reflux of
stomach contents. Also contributing to heartburn is the pressure of the enlarging uterus on the stomach, causing the reflux of stomach contents into the lower esophagus.
Gallbladder contractility is also slowed and this can result in gallstone production.
Hormone Changes
The following is a list of some of the effects hormones are thought to have on the body changes during pregnancy:
- Relaxes smooth muscle
- Softens ligaments
- Causes nausea
- Increases pigmentation
- Tissue swelling
- Hair loss
- Bleeding gums.
PHYSICAL CHANGES:
Swelling:
Swelling is common among the many-body changes during pregnancy, especially during the hot summer months.
Swelling and fluid retention during pregnancy is a body change that must be monitored during pregnancy as it can be a sign of complications associated with pregnancy,
(ie. preeclampsia, toxemia, gestational hypertension)
Increased pigmentation:
Any skin pigmentation on your body will very likely become more pronounced during pregnancy. Hyperpigmentation occurs because of increased melanocyte activity due to increased melanocyte-stimulating hormone.
Hemorrhoids:
Due to the changes in the cardiovascular system, blood gets channeled to areas of the body that are prone to the pooling of blood. These areas are called venous sinuses and are part of the venous system.
The most noticeable areas involved in this venous pooling are hemorrhoids (venous sinuses around the rectum and umbilicus), the labia and superficial leg veins (leg varicose veins). Though these vascular changes can pose medical problems, discomfort, and cosmetic concerns, these changes will almost always resolve after pregnancy. Cosmetic concerns can persist and this can be addressed well after the postpartum period.
Hair loss:
Hair loss is not uncommon postpartum and most often, will resolve over time. This is concerning to many new mothers. The problem is hormonal.
Bleeding gums:
Bleeding gums are often an incidental finding that pregnant women will notice when brushing their teeth. This is a hormonal problem and will resolve after pregnancy.
However, while pregnant, this irritation of the gums needs to be cared for to avoid gingivitis.
The important message here is to know that bleeding gums are observed during the course of a normal pregnancy.
Back Pain:
Back pain during pregnancy (aside from intermittent pain associated with contractions) is quite common. The frontal weight during pregnancy often leads to back strain and low back pain. The back muscles get overworked trying to correct your posture to maintain your center-of-gravity (balance).
In addition to muscle fatigue, pregnancy also causes hormonal changes to soften and loosen the pelvic ligaments to prepare for childbirth. Unfortunately, this hormonal effect results in joint instability and can lead to sciatic pain due to nerve compression.
Breast Changes:
Breast milk can leak during your pregnancy due to the physiologic changes caused by increased estrogen. This is often more pronounced with subsequent pregnancies.
Breast enlargement is caused by the development of milk ducts due to increased estrogen.
Increased pigmentation can occur around the areola.
Skin:
- Hyperpigmentation
- Stretch Marks
- Worsening acne
Pelvic Girdle Pain and Instability:
Ambulation can become difficult as the pelvic joints become less stable. Progesterone is softening and loosening the ligaments in the pelvis in preparation for childbirth.
Dietary Changes:
As a result of the many hormonal, intestinal and gastric changes, your diet will need to be adjusted to your tolerance level. For those with multiple gestations, the pressure pushing up under your ribs may cause more heartburn which may require you to sleep with your head elevated.
Varicose veins:
This problem can be either an observed physical change or functional change. For some, the superficial varicose veins during pregnancy never cause any functional problems.
However, there can be impaired function when varicose veins develop pain or swelling as a result of inflammation. This can lead to deep or superficial thrombosis (thrombophlebitis/blood clots). With deep vein thrombosis (DVT), there is a need for immediate medical intervention and treatment to prevent further blood clotting (heparin, Lovenox).
The observed physical changes associated with varicose veins involved with phlebitis are the following:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Induration (skin becomes firm)
- Tenderness
- Mottled appearance to the color of skin

*Signs of phlebitis must be brought to the attention of your provider immediately as the blood clotting can progress and cause blood clots to go the lung: pulmonary embolism. (This condition can be life-threatening.)
FUNCTIONAL CHANGES:
Constipation:
Constipation is primarily a result of the slowing of the intestinal tract by the hormone called progesterone. Progesterone effects smooth muscle cells which comprise the wall of the colon and are responsible for movement in the intestinal tract.
Urinary frequency:
Urinary frequency can have a few causes during pregnancy. Either from the pressure of the pregnancy on the bladder or from a urinary tract infection.
Concerns about a urinary tract infection must be taken seriously to prevent an infection from ascending into the upper urinary tract ( kidneys).
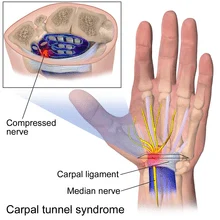
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Carpal tunnel syndrome is relatively common during pregnancy due to swelling associated with pregnancy. This swelling can put pressure on the median nerve as it passes through the wrist, resulting in the symptoms associated with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Sciatic Pain:
Sciatic nerve inflammation leading to sciatica can occur due to the same anatomic and physiologic changes attributed to the causes of low back pain. Namely muscle relaxation and loosening of the ligaments.
Heat Intolerance:
Heat intolerance is common during pregnancy, especially during the hot summer months.
In addition, there are many vascular changes that can contribute to heat intolerance.
Every effort should be made to maintain a normal core body temperature during your pregnancy. (This includes staying out of hot tubs, spas, and saunas.)
Sensory changes:
There are many women who describe changes in smell and taste during pregnancy.
Since taste is closely associated with one’s ability to smell, it is not surprising that these sensory symptoms may exist together. Many women describe losing their appetite for raw vegetables etc., and others describe the development of cravings (ie. pickles, ice cream).
There is a condition called Pica, where women will develop cravings for strange non-food items. Here is a link to learn more about Pica.
Fatigue:
Fatigue during pregnancy is common, in fact, it’s the norm! The following list, are just some of the reasons women experience fatigue as a result of the many material changes in anatomy and physiology previously discussed:
- Anemia
- Increased Metabolism
- Insomnia
- Decreased Mobility
- Musculoskeletal Demands
- Multiple Pregnancies (twins, triplets)
- Trying to maintain a prepregnancy schedule and not asking for help from family, friends or colleagues.

Tips to Manage Body Changes during Pregnancy
Swelling:
1. Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids.
Drinking water helps move fluids out of the tissues. Drinking water helps flush out toxins and decreases water retention.
If you can’t stand the taste of plain water, you may want to try infused water with fruits or pregnancy-safe herbs. Drinking lots of fluids will help keep your swelling related to body changes during pregnancy to a minimum.
This is our favorite water infuser: LA Organics Fruit Infuser Water Bottle
Here are a few recipes for infused water you may find helpful:
- Fruity Infused Water (52 Fruits Water Ideas) – Healthy Happy Smart
- 4 Fruit Infused Water Recipes – The Preppy Scientist

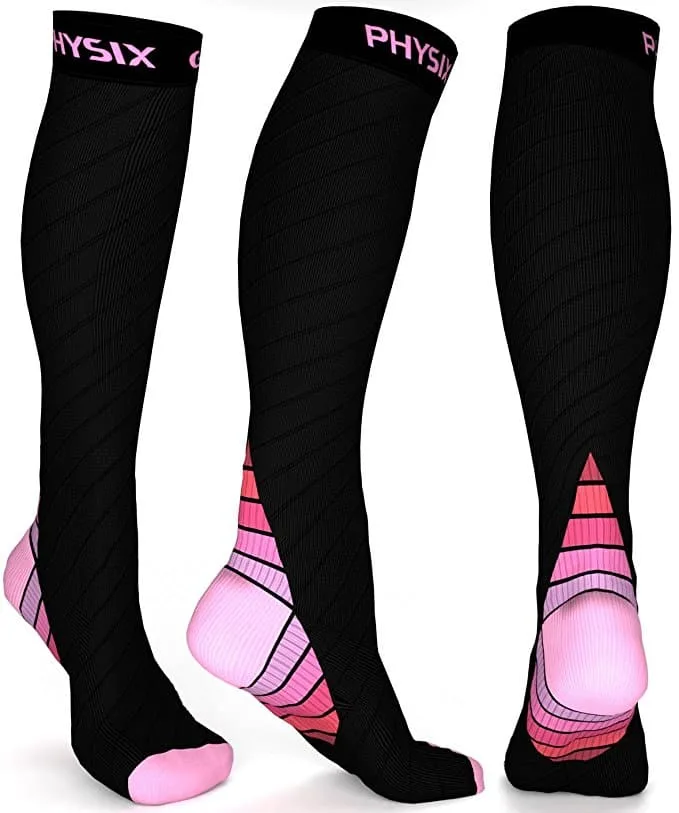
2. Compression Stockings:
Help prevent the pooling of blood in your legs. They feel amazing! They help with swelling and varicose veins. Athletes and runners swear by them and you will too!
3. Moderate Exercise: Be sure to clear with your provider.
Exercise helps to promote circulation and can help prevent blood clots. Walking and swimming are generally considered safe to do during pregnancy and can help with a host of pregnancy-related symptoms.
4. Reduce Salt Intake:
Most food is prepared with lots of salt, so try to avoid adding salt to your foods.
For more information on swelling during pregnancy: How To Prevent Swelling During Pregnancy
Hemorrhoids
1. Avoid sitting for long periods.
Try to keep moving as much as you can. Moving will help improve circulation to the area.
Try to get some exercise (once you clear it with your provider). Walking, swimming, and prenatal yoga can be good choices.
This is one of the most unpleasant body changes during pregnancy, but getting up and moving can really help minimize it.
2. Stay regular and avoid getting constipated.
This is by far the best thing you can do to avoid hemorrhoids. Drink plenty of fluids, eat more fiber and take a stool softener if necessary (ie. Colace).
3. Take a warm bath.
Soaking in a warm bath may help reduce your discomfort. It has the added bonus of being relaxing!
4. If your hemorrhoids are severe consider using a hemorrhoid donut to alleviate the discomfort.
For more information on hemorrhoids during pregnancy see American Pregnancy Association: Hemorrhoids During Pregnancy: Causes, Treatments, and Preventions
Bleeding Gums:
1. Though you may experience bleeding, continue to brush your teeth regularly.
Brush twice a day and floss regularly. Try not to be too aggressive with brushing as that can make your gums bleed even more. In most cases, keeping up with regular brushing results in less bleeding from the gums.
2. Use a soft toothbrush.
Make sure your toothbrush is labeled soft and not hard or medium. Though using a toothbrush is suggested even when not pregnant, it is particularly important if you have swollen gums as they can easily get irritated causing inflammation and a possible infection
3. If you experience discomfort use a toothpaste for sensitive teeth.
If discomfort persists you will want to see your dentist. Though gingivitis associated with pregnancy will resolve after your pregnancy, the inflammation of the gums can cause an infection.
4. Maintain routine dental care.
Don’t hesitate to contact your dentist if the bleeding does not diminish or you have concerns about gingivitis (inflammation of the gums). Fortunately, bleeding gums resulting from pregnancy almost always resolves after pregnancy
For more information on bleeding gums during pregnancy see BabyCenter: Bleeding Gums During Pregnancy
Back Pain:
1. Don’t lift heavy items.
It is easy to forget one’s physical limitations while pregnant. Hormones during pregnancy cause your pelvic ligaments and joints to loosen in preparation for childbirth. Unfortunately, joints throughout the body are affected making pregnant women more prone to musculoskeletal injuries.
Always bend at your knees to pick up items and divide items up into smaller loads to prevent back strain and low back pain.
Talk with your provider about using a maternity support belt to give your pelvis and lower back more support by redistributing the pregnancy weight. This can be a significant problem when carrying twins or triplets.
2. Practice relaxation techniques.
You can try meditation. Guided imagery or deep breathing to help you relax.
Relaxing may help relieve your back pain not only caused by musculoskeletal strain but also due to stress and anxiety.
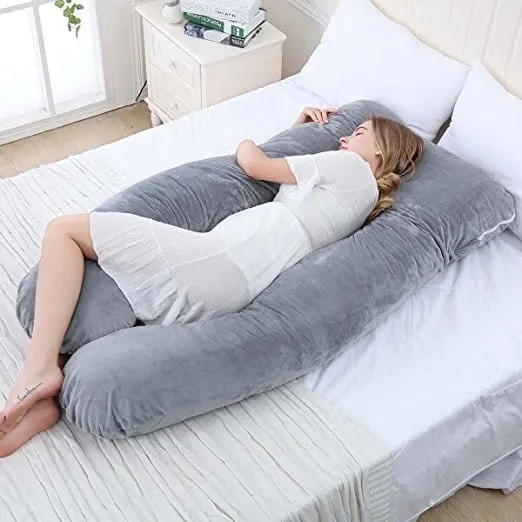
3. Sleep with a pregnancy pillow.
We can’t recommend pregnancy pillows enough! Pregnancy pillows can help you deal with many of the body changes during pregnancy.
Pregnancy pillows provide much-needed support for the tummy, shoulders, back, and legs. Pregnancy pillows can make sleeping on your side more comfortable too.
For more information about back pain during pregnancy: 8 Ways To Relieve Low Back Pain During Pregnancy
Fatigue:
1. Take Naps when you need too.
Pregnancy is very hard. The fatigue you feel is real. Naps are a great way to recharge and reboot yourself.
Fatigue is one of the most common body changes during pregnancy, especially during the first trimester, be gentle with yourself and rest when you need too.
2. Eat small, well-balanced meals several times a day.
Try to eat small meals. A large will leave you stuffed and looking for a nap. Try to balance your carbs and proteins. Avoid sugary snacks like candy bars.
They will give you an immediate energy burst but will make you feel even more fatigued just a few hours later.
3. Say “No” and do not feel guilty about it.
Saying “No” can be difficult. If you are feeling fatigued try to limit social outings and errands as much as possible.
Be gentle and flexible with yourself. Your friends and family will understand.
For more information about fatigue during pregnancy: 10 tips To Fight Fatigue During Pregnancy
Varicose Veins:
1. Do not cross your legs while sitting.
When you cross your legs, the pressure on the veins in your legs can block the free flow of blood up to your heart. Blood returning to the heart from your legs is already dealing with the forces of gravity. The pooling and slowing of blood flow in the legs should always be avoided. Though varicose veins may be a “theoretical” concern, even worse is the risk of blood clots during pregnancy. The best thing you can do for your legs during pregnancy is to elevate them whenever possible. This can also dramatically reduce swelling in the ankles at the end of the day, as long as the swelling is not related to a pregnancy complication such as toxemia (high blood pressure).
2. During prolonged trips by car or plane, try to stand frequently and walk around.
This will help your muscles contract and return blood to your heart. This helps you avoid developing blood clots.
3. Wear compression stockings.
They really are amazing. They will help reduce swelling due to fluid retention from being on your feet all day. Discuss the right sizing with your provider.
For more info about varicose veins during pregnancy: How To Deal With Varicose Veins During Pregnancy
Constipation:
1. Drink plenty of fluids.
Drink 10 to 12 cups of fluid a day. Drink, water, milk, or sparkling broth. Keep a full water bottle with you at all times. This will help you remember to drink.
2. Eat a high fiber diet.
Consume 30 grams of fiber a day. Good choices for fiber-filled foods include fruits, vegetables, breakfast cereals, and bread.
3. Eat Plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Bananas, apples, leafy greens, avocados make good choices and can help you avoid constipation which can be one of many common functional body changes during pregnancy.
For more information on preventing constipation during pregnancy see Healthline: 5 Safe Remedies For Constipation During Pregnancy
Carpal Tunnel
1. Rest your hands whenever possible.
Often times, you may not realize how much you use your hands for texting, computer work, etc.. Make a conscious effort to periodically rest your hands.
2. Immobilize your wrist/hand.
This is particularly important if your healthcare provider has performed a neurology exam and diagnosed you with carpal tunnel syndrome.
Immobilization is best achieved by using a wrist brace. Years ago, finding a wrist brace was difficult, now you can often get one at your provider’s office or you can order one online.
There are many to choose from online: Wrist Braces On Amazon
3. Avoid activities that are repetitive and make your symptoms worse.
Though these activities may be routine (typing, cooking, etc.) and never cause you problems. When pregnant, these same activities cause symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome because the swelling associated with pregnancy puts increased pressure on the median nerve.
For more information about carpal tunnel syndrome during pregnancy: How To Relieve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome During Pregnancy
Dehydration:
1. Drink more water.
Drink 8-12 cups of water a day to keep yourself well-hydrated during pregnancy. You can drink juice, milk, and broth too. Be sure to drink pasteurized milk and juice to avoid any type of bacteria that could harm you or your baby.
2. Limit your caffeine intake.
For many years there has been a lot of discussion about caffeine during pregnancy. At the time of this article, it is best to limit caffeine intake to 200mg a day. Keep in mind that there are many sources of caffeine so you will want to consider how much you are getting from coffee, tea, soda, chocolate, etc.. throughout the day,
3. Ice pops, popsicles, and Pedialyte pops can help you increase your fluids.
This can be especially true during the first trimester if you have morning sickness. It isn’t uncommon to have morning sickness, food aversions, and fatigue which causes you to not consume enough fluids.
4. Avoid direct heat.
When outside during the hot summer months (beach, boating, etc.), sit in shaded areas or use a sun umbrella. During pregnancy, when you are in hot weather, your increased metabolic rate and dilated blood vessels increase your core body temperature.
You want to keep your core body temperature low especially during early fetal development. Keeping your core temperature low will also prevent dehydration.
For more information about dehydration during pregnancy: How To Prevent Dehydration During Pregnancy
Conclusion:
There are many body changes during pregnancy and you will undoubtedly receive many strong opinions about how to manage them. These opinions will come from family members, friends, and coworkers. People in your life who will want to share what worked for them, even though you never asked. What worked for them may not work for you.
So when it comes to dealing with body changes during pregnancy … do what you want to do as long as it is supported by your prenatal care provider.